By 2050 the U.S. power grid could nearly double in capacity, with most of the newly built capacity coming from renewable sources such as solar and wind to meet energy demand, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) said this week.
The continued rise of renewables is expected to come as capital costs fall for battery storage, solar panels and wind turbines and government subsidies make renewables more cost effective when building new power capacity.
The outlook was based on outlook case studies included in the EIA’s recently released Annual Energy Outlook 2023.
“In the Reference case, we project a large increase in renewable capacity of about 380% from 2022 through 2050,” the EIA said. “By comparison, fossil fuel generating capacity, which includes coal and natural gas-fired power plants, increases about 11%.”
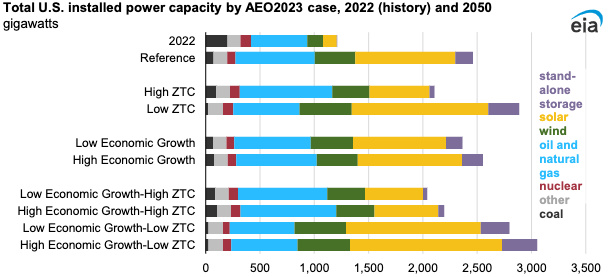
Renewable capacity shows the most growth, increasing nearly 600% during the outlook period in the High Economic Growth and Low Zero-Carbon Technology Cost combination case.
Renewable capacity is even projected to grow in the Low Economic Growth and High Zero-Carbon Technology Cost combination case by nearly 230%, according to the EIA.
RELATED
Analysts: Global Wind Capacity Approaches 1 TW as Offshore Grows
The outlook was released as companies in the U.S. and abroad continue working on renewable and low-carbon projects to lower emissions. Here’s a look at some of this week’s renewable energy news.
Geothermal
Geothermal Technologies Pursues Project in Denver-Julesburg Basin
Baltimore-based Geothermal Technologies Inc. (GTI) said on April 11 it has filed for permits to drill geothermal wells in the Denver-Julesburg (D-J) Basin in Weld County, Colorado.
The move is part of the company’s efforts to build a first-of-its-kind geothermal power plant in the D-J using the company’s proprietary technology, GTI CEO Gary McDaniel said in a news release.
“We are excited about the potential that exists in Colorado for the development of advanced geothermal power,” McDaniel said. “GTI has calculated that the thermal prospect in the D-J Basin has over 5 GW [gigawatts] of geothermal energy that can be harvested using our technology.”
GTI’s field development plan shows it can install up to 400 megawatts (MW) of baseload electricity production, he added.
Called GenaSys, the company’s technology is paired with advanced Organic Rankine Cycle power generation technology to more efficiently extract geothermal energy.
The permits were filed with Colorado’s Division of Water Resources.
Hydrogen
Amp Energy to Develop 5-GW Green Hydrogen in South Australia
Carlyle portfolio company Amp Energy is teaming up with Iron Road Ltd. to develop a green hydrogen project in South Australia, according to an April 12 news release.
The hydrogen at scale project is located in the Cape Hardy Port Precinct, which has direct access to existing transmission infrastructure and a deepwater port.
Amp Energy said it plans to develop and build up to 5 GW of electrolyzer capacity during the next decade in the precinct to deliver more than 5 million tons per annum (mtpa) of green ammonia.
“Our background of developing large scale upstream power systems globally positions Amp for the emerging opportunity of green hydrogen and provides industrial synergies,” said Paul Ezekiel, co-founder and CIO of Amp. “The development of strategically located, transmission-connected green hydrogen and ammonia facilities at select locations such as Cape Hardy in South Australia is critical to our continued global growth and long-term strategy.”
The project is among several renewable energy moves that the company, known for its global energy transition development platform, has taken in recent years. In 2021, Amp established the AUD$2 billion (US$1.34 billion) Renewable Energy Hub of South Australia, focused on renewable generation and battery energy storage.
Sinopec to Build China West-to-East Green Hydrogen Transmission Pipeline
China’s Sinopec will build a pipeline to transfer hydrogen from renewable energy projects in China’s northwestern Inner Mongolia region to cities in its east, according to a report in state media outlet Xinhua on April 10.
The pipeline will stretch 400 km from Ulanqab in sparsely populated Inner Mongolia to the capital Beijing and will have an initial capacity of 100,000 tonnes per year, said the report, citing Sinopec chairman Ma Yongsheng.
Ports will be built along the pipeline to allow access to new potential hydrogen sources, the report added.
While the country already operates pipelines for so-called gray hydrogen produced from fossil fuel sources, the project is the country’s first “West to East” green hydrogen transmission line, according to the report.
Solar
Lightsource BP Closes Financing for Arkansas Solar Project
Lightsource BP said on April 11 it closed a $327 million financing package for a solar project to be constructed under a build-transfer agreement with Entergy Arkansas.
Located near Osceola in Mississippi County, Arkansas, the 313-MW Driver Solar project will be the largest in Arkansas and the largest in Entergy Arkansas’ portfolio when it is complete. The project is expected to generate enough electricity to power more than 50,000 homes, according to Lightsource BP.
“One of our key commitments to customers is to help them find economic solutions to meet their sustainability goals,” Entergy Arkansas CEO Laura Landreaux said in a news release.
Lenders helping to make the project possible included HSBC Bank USA, National Association (HSBC Bank USA N.A.), part of HSBC Group; BNP Paribas; Societe Generale and Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corp.
The solar project is located adjacent to U.S. Steel’s Big River Steel facility and its $3 billion expansion project. “The energy generated will be used throughout the facility, including the production of our verdeX steel, which is produced with fewer emissions and with up to 90% recycled material,” said Daniel R. Brown, COO and senior vice president of advanced technology steelmaking for Big River Steel.
Dominion Energy Plans to Buy Solar Project in Virginia
Electric utility company Dominion Energy Inc. said on April 11 it will buy Longroad Energy’s 108-MW Foxhound solar project in Virginia.
The project, which has long-term power purchase agreements in place, has been in development for six years and will produce enough clean energy to power more than 17,000 homes, Longroad said in a news release.
First Solar is supplying Series 6+ solar modules for the project, Nextracker is supplying trackers and TMEIC is supplying solar inverters.
The deal’s financial details were not disclosed. Financial close of the acquisition is expected upon mechanical completion of the project in January 2024.
Arctech Lands 1.5-GW Solar Tracker Order for Saudi Solar Plant
Solar tracker manufacturer Arctech has expanded into Saudi Arabia, having secured a 1.5-GW solar tracker deal for the ASB solar project in Saudi Arabia.
The order for Arctech’s 1.5-GW SkyLine II solar tracker marks the company’s first solar tracking and racking project in the country, it said.
Located in the Al Shubakh district, Jeddah City, the solar project is being developed by ACWA Power and EPC China Energy Engineering Group Co. Ltd. Developers said the ASB project is the largest solar project under construction in Saudi Arabia.
Wind

IberBlue Gears Up for 1.96-GW Floating Wind Projects Off Spain, Portugal
Iberia-focused IberBlue Wind has unveiled plans for two floating wind projects with a combined installed capacity of 1.96 GW off the Spanish-Portuguese border, the company said on April 11. The projects generate enough to power more than 1 million homes.
Called Juan Sebastián Elcano and Creoula, the wind projects will have a total of 109 turbines spanning across 530 sq km off the coasts of Baixo Miño in Pontevedra and Viana do Castelo, IberBlue said.
The projects will help move the joint venture (JV) company—comprised of Simply Blue Group, Proes Consultores and FF New Energy Ventures—closer to its goal of developing about 2 GW of offshore wind energy capacity off the peninsula.
“It is very exciting to develop cross-border floating offshore wind projects and to collaborate with both Portuguese and Spanish governments on this positive opportunity for both countries,” said IberBlue Wind Vice President Adrián deIber Andrés. “We have already engaged with both authorities when we presented our projects to the Spanish and Portuguese authorities, and we look forward to continued engagement.”
Elcano, the smaller of the two wind farms, will have 29 turbines, and Creoula will consist of 80 turbines. Each turbine will be 18 MW.
“It is estimated that the cost of their joint development could be 32% lower than if they were to be developed separately,” IberBlue said in a news release. “This will maximize synergies in resourcing and economies of scale during both the construction phase and operation phases, consequently reducing energy prices for both countries, which operate as one within the Iberian Electricity Market—MIBE.”

Scottish Waters Home to ‘World’s Deepest’ Wind Turbine Foundation
What is being called the world’s deepest wind turbine foundation, or jacket, has been installed at a depth of 58.6 m (192.3 ft) at the 1.1-GW Seagreen Wind Farm offshore Scotland, SSE Renewables said on April 12.
After being transported by a Seaway 7-operated barge, each of the 2,000-tonne turbine foundations were lifted into place by the Saipem 7000 semisubmersible crane vessel. Each foundation will support a Vestas V164 10-MW turbine, SSE said.
The installation broke the company’s previous record of 57.4 m (188.3 ft).
“The significant milestone also marks the installation of the 112th jacket at the 114-wind turbine wind farm, which is a £3 billion [$US3.72 billion] JV between SSE Renewables and TotalEnergies,” SSE said in a news release. “The final wind turbine foundation is expected to be installed later this week.”
The wind farm is expected to begin commercial operations later this year, producing enough electricity to power more than 1.6 million homes in the U.K.
Havfram Wind Lands Work for 1.6-GW Nordseecluster
RWE and Northland Power have selected Havfram Wind as the preferred supplier to transport wind turbines for the wind cluster the two companies are jointly developing offshore Germany.
Havfram’s scope of work will include transporting and installing at least 104 15-MW Vestas offshore wind turbines destined for the 1.6-GW Nordseecluster, which will be developed in two phases subject to final investment decisions.
Developers said Nordseecluster will consist of four wind farm sites in the German North Sea, together producing enough electricity to annually power 1.6 million German households.
Plans are to begin turbine installation at sea in 2026, with commercial operations starting in early 2027, according to the release.
OX2, EEW Seal Monopile Agreement for Wind Farms Offshore Sweden
OX2 has tapped Germany-based EEW Special Pipe Constructions GmbH & Co. (EEW) to provide monopiles for two wind farms being developed off Sweden’s west coast, according to an April 13 news release.
EEW will deliver up to 230 monopile foundations for the Galatea-Galene and Triton offshore wind farms, according to the agreement. The wind farms are among three OX2 is developing with Ingka Investments. The other, Aurora, will be developed between the islands Gotland and Öland, OX2 said in the release.
“We will be working close with EEW to make sure we can start construction as soon as possible and thereby make a large-scale contribution of emissions-free electricity to parts of Sweden that needs it the most,” said Emelie Zakrisson, head of offshore wind development for OX2 Sweden.
Once complete, the Galatea-Galene project will produce about 6 terawatt hour (TWh). In the Baltic Sea, Triton will have a production capacity of about 7.5 TWh and Aurora at 24 TWh.
Reuters contributed to this article.
Recommended Reading
Chevron Hunts Upside for Oil Recovery, D&C Savings with Permian Pilots
2024-02-06 - New techniques and technologies being piloted by Chevron in the Permian Basin are improving drilling and completed cycle times. Executives at the California-based major hope to eventually improve overall resource recovery from its shale portfolio.
CEO: Continental Adds Midland Basin Acreage, Explores Woodford, Barnett
2024-04-11 - Continental Resources is adding leases in Midland and Ector counties, Texas, as the private E&P hunts for drilling locations to explore. Continental is also testing deeper Barnett and Woodford intervals across its Permian footprint, CEO Doug Lawler said in an exclusive interview.
CNX, Appalachia Peers Defer Completions as NatGas Prices Languish
2024-04-25 - Henry Hub blues: CNX Resources and other Appalachia producers are slashing production and deferring well completions as natural gas spot prices hover near record lows.
To Dawson: EOG, SM Energy, More Aim to Push Midland Heat Map North
2024-02-22 - SM Energy joined Birch Operations, EOG Resources and Callon Petroleum in applying the newest D&C intel to areas north of Midland and Martin counties.
For Sale, Again: Oily Northern Midland’s HighPeak Energy
2024-03-08 - The E&P is looking to hitch a ride on heated, renewed Permian Basin M&A.






