The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Loan Programs Office closed on a $3 billion partial loan guarantee for Houston-based Sunnova Energy International’s Project Hestia, which aims to give disadvantaged homeowners and communities more access to clean power.
The DOE conditionally committed to the loan in April and closed the partial loan guarantee Sept. 28. The loan equates to a 90% guarantee of up to $3.3 billion of term loans, Sunnova said in a news release.
“Today marks the beginning of an exciting chapter in our pursuit of a cleaner and more equitable energy landscape,” Sunnova CEO William J. Berger said.
Through the 568-megawatt (MW) capacity Project Hestia, Sunnova will make available rooftop solar, battery storage and virtual power plant (VPP)-ready software available during the next 25 years. The smart software, app and portal aims to not only lower emissions but also “enhance the informed use of load controllers and smart appliances, and support grid stability by giving consumers near real-time insight into their residential energy system and quantifying the location-specific emissions impact of changes in consumer behavior,” Sunnova said.
As part of the project, loans for clean energy systems for between 75,000 and 115,000 U.S. homeowners will be available, the DOE said. The project could avoid an estimated 7.1 million tonnes of CO2, roughly equivalent to eliminating such emissions from 1.5 million vehicles.
Sunnova expects the loan guarantee agreement to “support over an estimated $5 billion in Sunnova loan originations, reduce the company’s weighted average cost of capital, and generate interest savings.”
Plans are to utilize it in fourth-quarter 2023 for Hestia 1.
“This is an important step in structured solar investments that will accelerate solar adoption and bring our best-in-class service to more underrepresented customers,” Sunnova CFO Robert Lane said.
Energy Storage
Azincourt Energy Discovers ‘Significant’ Pegmatite Field in Canada
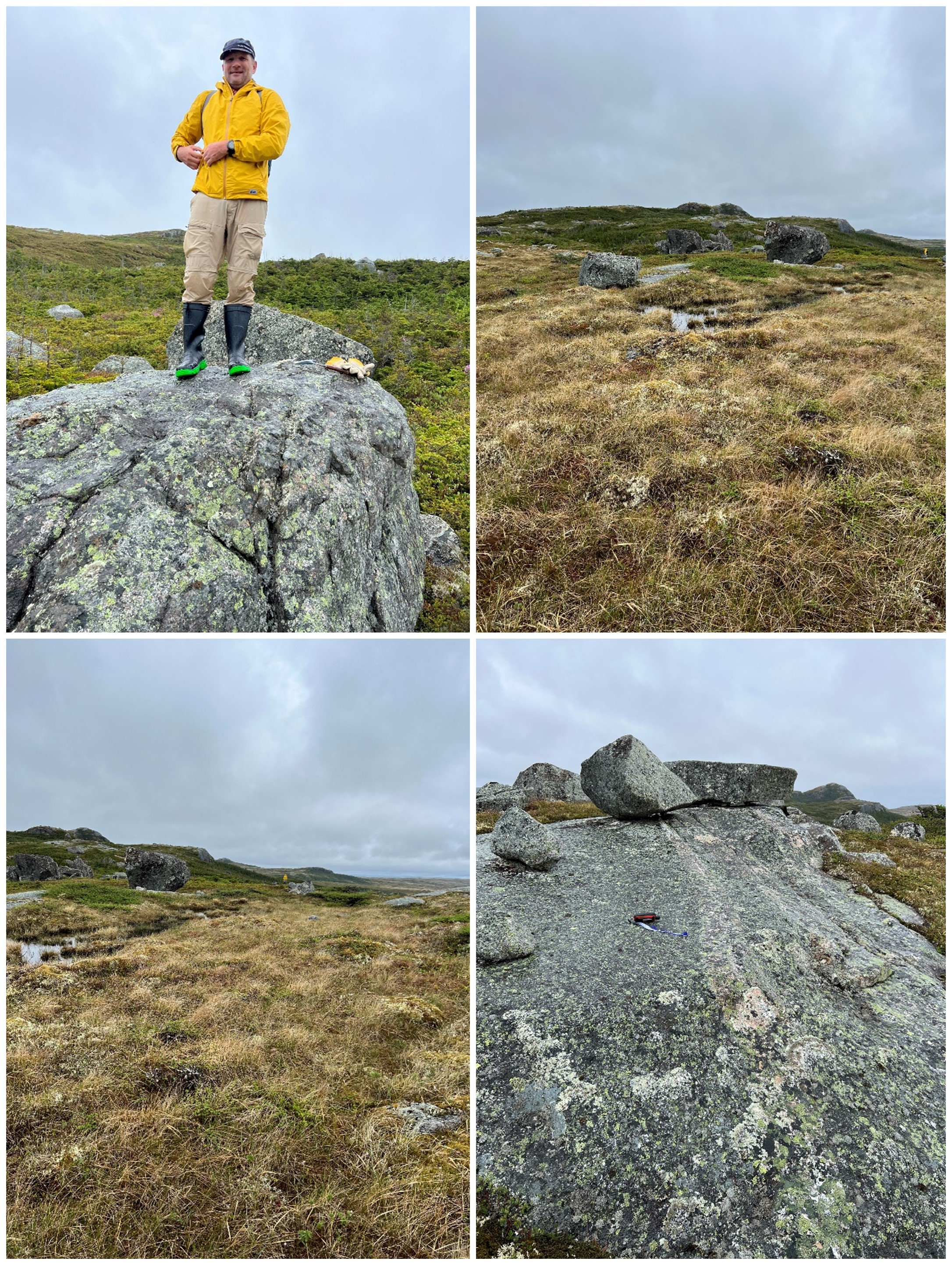
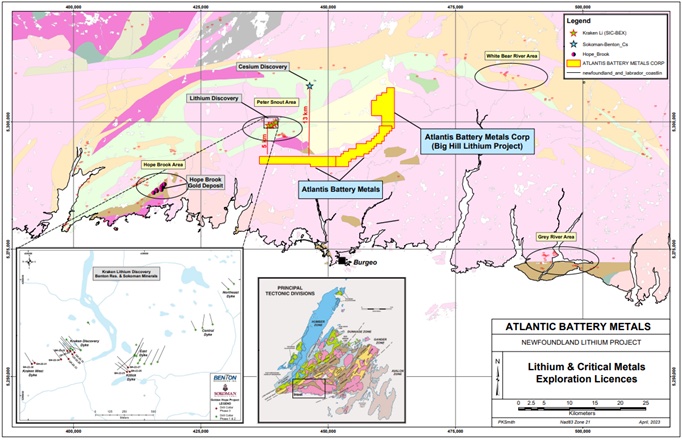

Vancouver-based Azincourt Energy said on Sept. 26 that it discovered a significant pegmatite field during initial exploration for its Big Hill Lithium project in southern Newfoundland, Canada.
Lithium, a key mineral used to make batteries such as for electric vehicles and electronics, can be extracted from pegmatite, which is an igneous rock or crystalline granite. The company said pegmatites were identified around a government mapped mafic unit with an estimated age of Late Silurian.
“The first round of exploration on the Big Hill Project was successful in identifying pegmatites on the property,” Trevor Perkins, vice president of exploration for Azincourt, said in a news release. “The area is significantly underexplored and will require additional detailed work to examine the pegmatites identified, the extents of the systems and determine if there are lithium bearing phases within the system. … We have barely scratched the surface on examining the property.”
Located south of the Benton Resources Inc. and Sokoman Minerals Corp. joint venture’s Kraken Lithium Pegmatite Field discovery, Big Hill consists of three contiguous exploration licenses with a combined 300 claims covering 7,500 hectares. The pegmatite field was discovered in the southern edge of claim 035342M, which spans for about 400 m trending north-northeast, Azincourt said.
As part of the helicopter-assisted exploration program, a team of five geologists and one prospector collected about 70 bedrock samples. Azincourt’s partner Atlantis Battery Metals Corp. conducted the initial exploration program.
Azincourt is considering additional exploration, which may be split into two phases. Phase 1 would involve helicopter-assisted prospecting, geological mapping and geochemical sampling, plus a preliminary geochemistry survey for lithium-cesium-tantalum pegmatite lithium path-finder elements among other tasks. Based on the Phase 1 results, a second phase would involve high-resolution geophysical and drone surveys, selected trenching and an initial 1,500-m diamond drilling program.
Oil States Lands Contract for Deepsea Mineral Riser System
Houston-based Oil States International Inc. (OSI) said it sealed a contract for its Merlin Deepsea Mineral Riser system, which will be used to harvest critical minerals such as cobalt, manganese and nickel from the seafloor.
The company that awarded the contract was not disclosed.
OSI leaned on its more than 40 years of deepwater offshore experiences to develop the system for deepsea mineral recovery. The Merlin riser system enabled The Metals Co. and Allseas to collect more than 3,000 tons of polymetallic nodules in 2022. Found on the seabed, polymetallic nodules contain base metals needed to make batteries for electric vehicles, solar cells, wind turbines, computers and smartphones.
“We are very proud of the industry's recognition of our expertise and the technologies we have developed to enable pathways toward a lower-carbon multi-source energy mix to meet growing global energy demands,” OSI President and CEO Cindy B. Taylor said Sept. 14 in a news release. “We are connecting the energy future by leveraging our rich oil and gas heritage to support the development of additional energy sources while augmenting our core technologies, setting the stage for longer-term growth.”
Geothermal
Fervo Breaks Ground for Geothermal Drilling Campaign in Utah
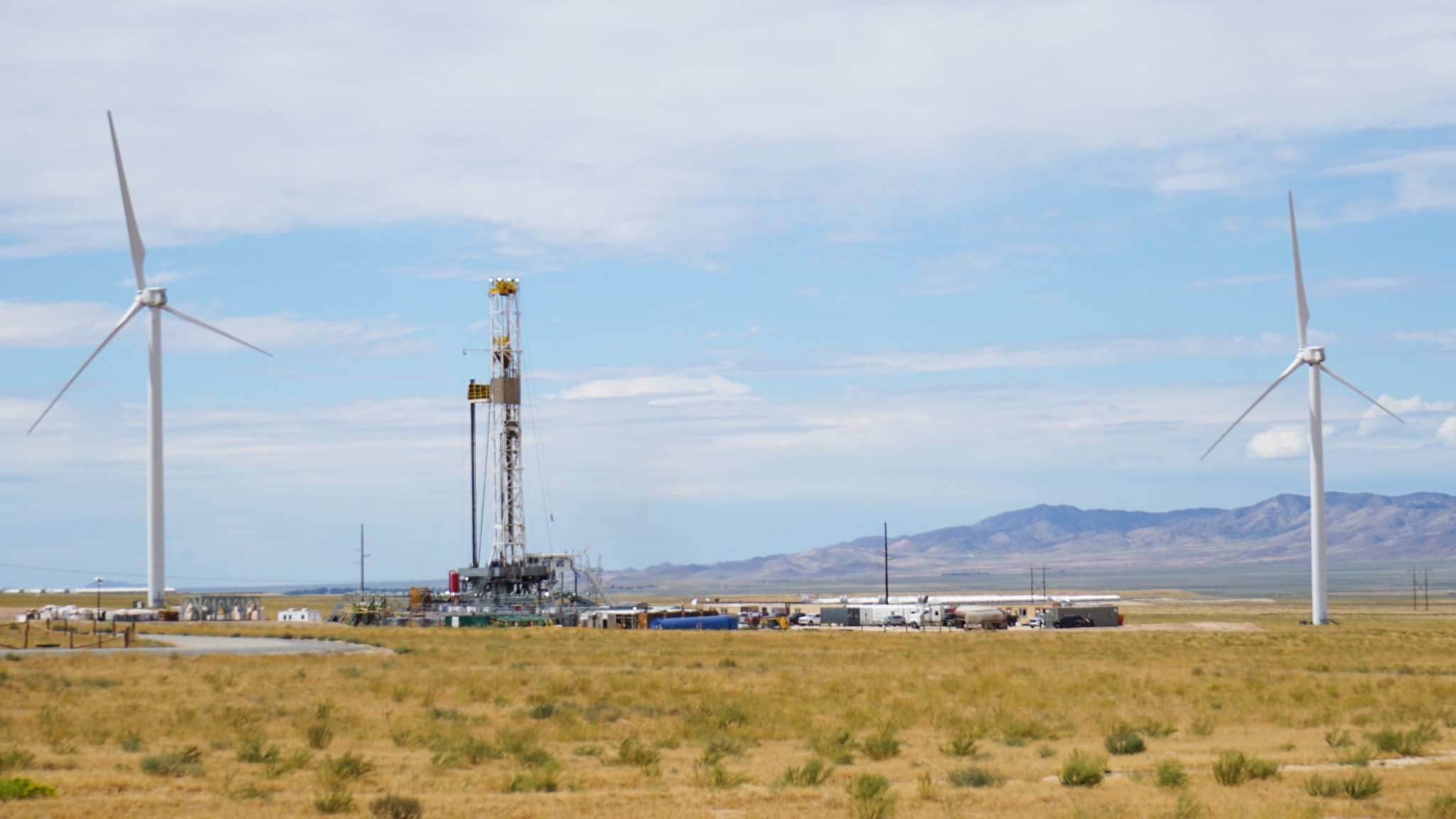

Geothermal technology company Fervo Energy has kicked off an exploration drilling campaign, ceremoniously breaking ground Sept. 25 at its Cape Station project in Beaver County, Utah.
The geothermal company said it aims to deliver 400 MW of 24/7 carbon-free electricity from the project, bringing power to the grid in 2026 and fully scaling production in 2028.
“Beaver County, Utah is the perfect place to deploy our next-generation geothermal technology,” Fervo CEO Tim Latimer said in the release.
Researchers estimate southwest Utah has more than 10 GW of high-quality geothermal reserves, according to Fervo. The state has been the site of research carried out over the last six years by the DOE’s Frontier Observatory for Research in Geothermal Energy (FORGE).
“Thanks to cutting edge research and data collection from FORGE, Fervo can accelerate the production of the region’s geothermal resources,” he added.
In July, Fervo said the company proved the commercial viability of its drilling technology—which uses oil and gas horizontal drilling techniques—to capture geothermal energy. Utilizing multistage, plug-and-perforate stimulation treatment design with proppant to improve the permeability of horizontal wells, the 30-day well test resulted in an enhanced geothermal system (EGS) record-setting flow rate of 63 liters per second, which made way for a record EGS output of 3.5 MW of produced electricity, the company said.
Hydrogen
Mitsubishi Power Installs 5.5-MW Electrolyzer in Japan
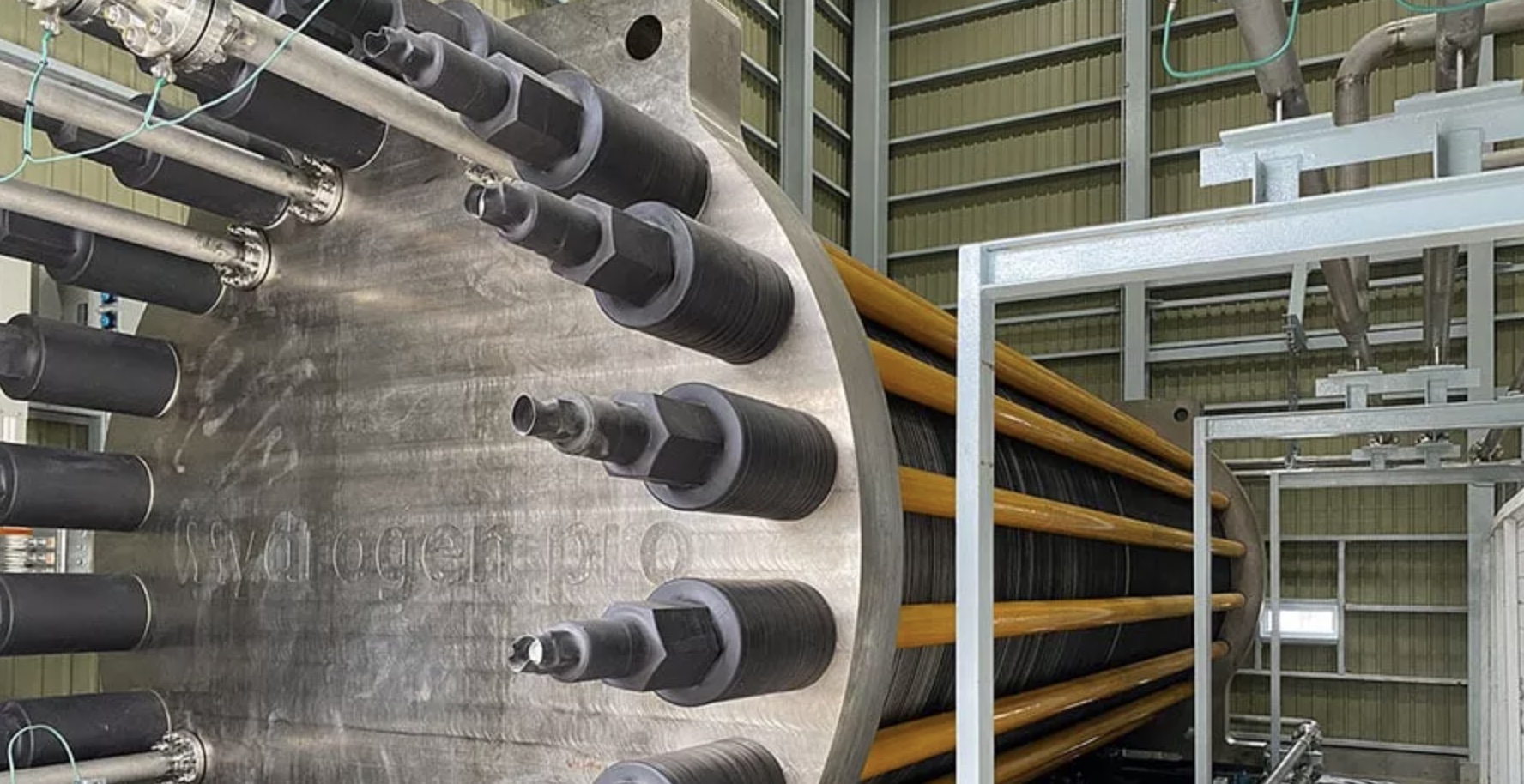

Mitsubishi Power has permanently installed a 5.5-MW single stack pressurized alkaline electrolyzer at the Takasago Hydrogen Park in Japan for long-term validation, the company said on Sept. 28.
The two-phase validation process started at the Herøya Industrial Park in Norway, where a unit and short-term validation ended in a 96-hour baseload run of safe and reliable operation, Mitsubishi said. The second long-term validation began with the permanent installation at Takasago.
“These validation units are significant milestones for our electrolyzer technology and a testament to how we approach the development of our products for our customers,” Kent Rockaway, vice president of hydrogen production for Mitsubishi Power Americas, said in a news release.
Plans are to use the electrolyzer design to produce green hydrogen at the Advanced Clean Energy Storage (ACES Delta) project, which is being jointly developed in Utah by Chevron and Mitsubishi Power Americas. Equipment is scheduled to begin arriving in fall 2023 to produce green hydrogen and store it in two large salt caverns until it is needed for dispatch back to the grid.
DHL, Sasol Join Hydrogen Firm HH2E on Sustainable Jet Fuel Project
German logistics giant DHL is teaming up with energy firm HH2E and South African petrochemicals firm Sasol on the expansion of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) production in Germany, HH2E said on Sept. 25.
The companies have signed an agreement to set up a joint initiative to build potential production capacities for SAFs based on green hydrogen, or eSAFs, somewhere in eastern Germany, HH2E said in a news release.
They plan production of at least 200,000 tonnes per year, with the potential to scale up to 500,000 tonnes per year, it added.
Aircraft manufacturer Airbus also intends to join the consortium to use the jet fuel, according to the statement.
Solar
BP Starts Construction of Texas Peacock Solar Project
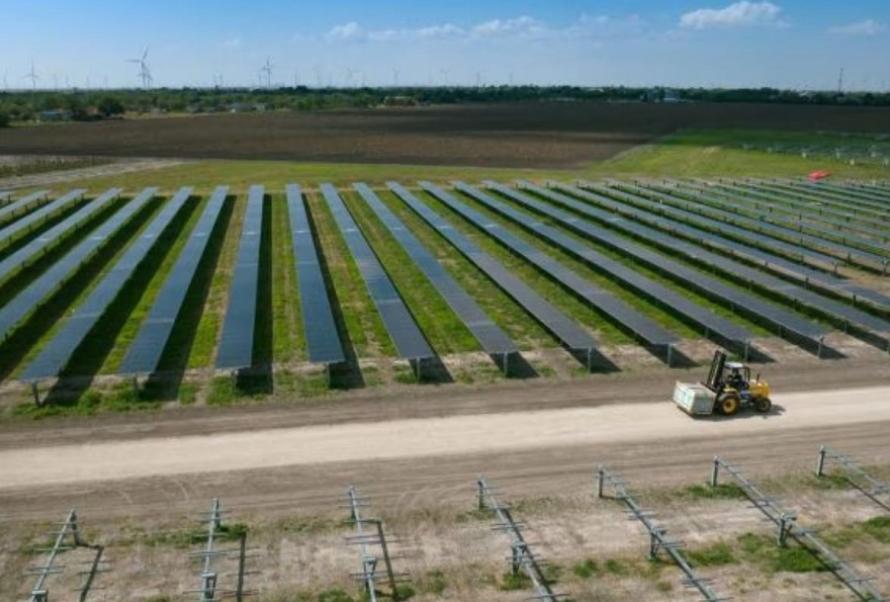

BP began construction of its 187-MW direct current Peacock Solar Project just north of Corpus Christi in San Patricio County, Texas, BP said in a Sept. 26 press release. The project is part of the company’s plans to invest in and build renewable energy capacity of 50 gigawatts by 2030.
The renewable electricity generated from the project—enough to power the equivalent of 34,000 homes—will be sold under a long-term power purchase agreement to Gulf Coast Growth Ventures, a joint venture between Exxon Mobil and SABIC. The facility produces materials for the manufacture of clothes, food containers, packaging, agricultural film and construction materials.
Lightsource BP, BP’s 50-50 joint venture partner, is developing and managing the construction of Peacock on behalf of BP. PCL Construction, the main engineering, procurement and construction contractor for the project, will install First Solar low-carbon solar panels and GameChanger Solar trackers.
Peacock will also have vegetation beneficial to pollinators and other wildlife planted under and around its solar panels and sheep grazing around the site to keep farmland in production and soil healthy.
“Securing this agreement and kicking off construction of Peacock helps support the transition to lower carbon energy, while benefiting local communities and the economy,” Dave Lawler, BP America chairman and president, said in the press release. “It’s another way BP is accelerating growth of our U.S. solar generation capacity, investing in America and advancing our transformation to an integrated energy company.
Wind
Ørsted Cranks Up 200-MW Wind Farm in Kansas
The 200-MW Sunflower Wind farm initiated operations in Marion County, Kansas, Ørsted said Sept. 29, bringing to 13 the company’s operational wind farm count in the U.S.
The wind farm, which will use a new aircraft detection lighting system to reduce light pollution for residents, has the capacity to power more than 70,000 homes.
“We’re thrilled to celebrate this achievement and our first clean energy project in Kansas with the community, legislators and our participating landowners,” said David Hardy, group executive vice president and CEO of Region Americas for Ørsted. “With Sunflower Wind, we now have 13 operational wind farms in the U.S., generating 832 MW in the Southwest Power Pool.”
In connection with the project, Ørsted said it also “pioneered a landmark supply chain decarbonization effort to deliver renewable energy access and bundled renewable energy credits from Sunflower Wind to nine companies.”
Ørsted, working with Schneider Electric, said it entered power purchase agreements with Amcor, PepsiCo, Stryker, Citizens and Walmart’s Project Gigaton cohort, which includes Amy’s Kitchen, Great Lakes Cheese, The J.M. Smucker Co., Levi Strauss & Co. and Valvoline Global Operations.
BOEM Completes Environmental Review of Dominion’s Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind
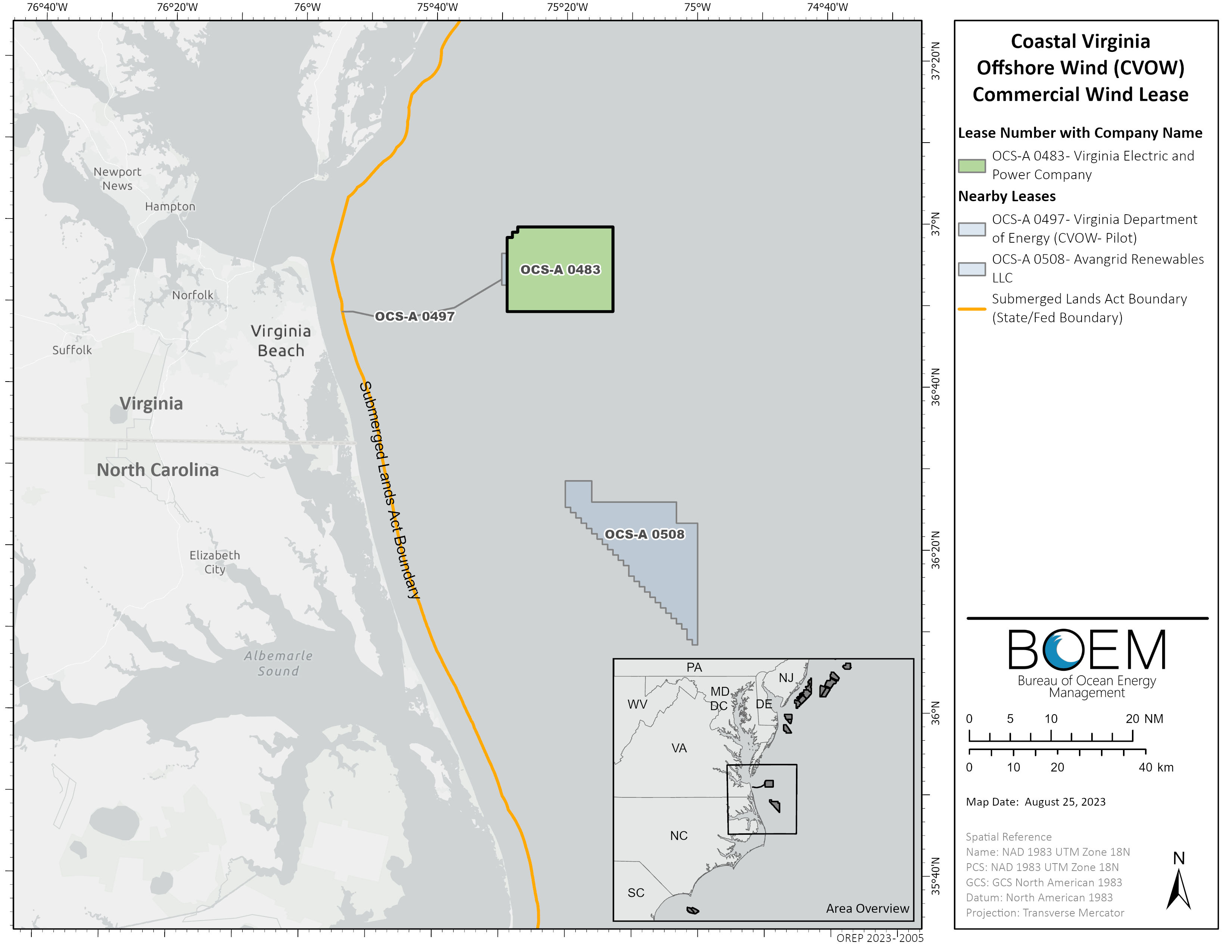
The U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) said Sept. 25 it has completed the environmental review of Dominion Energy’s planned 2.6 GW Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind (CVOW) project, marking a regulatory milestone for the largest offshore wind project being developed in the U.S.
With 176 wind turbines each with a capacity of 14.7 MW, the project—located on a 112,800-acre commercial lease area off Virginia Beach—is expected to produce enough electricity for 660,000 Virginia homes, Dominion Energy said.
A notice of availability for the final Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) for the proposed project was published in the Federal Register on Sept. 29. The final EIS analyzes the potential environmental impacts of activities in the project’s construction and operations plan, BOEM said. The EIS is available on BOEM’s website.
BOEM’s Record of Decision on whether to approve the project is expected this fall.
“Today’s announcement reinforces the confidence that the company, our vendors and our suppliers have in our project’s completion, providing further motivation to maintain focus on delivering on time and on budget knowing we and our government partners continue to meet critical milestones,” Dominion Energy CEO Bob Blue said.
Completion of the environmental review comes as the U.S. aims to deploy 30 GW of offshore wind energy capacity by 2030. Earlier this month, BOEM completed environmental analysis for the proposed Empire Wind Farm project being jointly developed offshore New York by Equinor and BP. The project includes Empire Wind 1 with up to 57 wind turbines and Empire Wind 2 with up to 90 wind turbines, together generating about 2 GW of renewable energy.
Alcazar Energy to Invest $200MM in Montenegro Wind Farm
Renewable energy investor Alcazar Energy on Sept. 28 announced it plans to invest $200 million in building a 118-MW wind park in Montenegro, which would be the largest such farm in the Adriatic country.
The Bijela wind park in Montenegro’s northwest would be the first investment under the company’s strategy to build a portfolio of renewable energy projects in the western Balkans, worth $600 million, Alcazar Energy CEO Daniel Calderon told Reuters.
On Sept. 28, the company signed a deal to acquire the rights to Bijela from two local companies—Simes Inzenjering and Sistem MNE—which were the developers of the project.
“Our local partners are experienced in renewable projects, they will ensure the project follows all the local rules ... and we shall bring the capital, lenders, equity, contractors and international technology,” Calderon said.
He said the project is expected to reach its financial close by the first quarter of 2025, when the construction should begin. The farm is expected to be in operation in 2026 or 2027.
Vestas Wins Polish Order for 76 Offshore Wind Turbines
Denmark’s Vestas has won an order from Poland’s Baltic Power for 76 offshore wind turbines with an overall capacity of 1,140 MW, the companies said in a statement on Sept. 28.
The companies did not disclose the value of the order.
In August, Vestas said it aims to turn a profit this year after struggling to recover from supply chain problems, high raw material costs and a mounting backlog.
The Danish company will begin delivering the turbines that come with the 15-year service agreement during the first three months of 2025, with power production expected to start in 2026.
Baltic Power is owned by Polish oil refiner Orlen and Canadian power producer Northland Power.
Hart Energy Staff and Reuters contributed to this report.
Recommended Reading
Shipping Traffic Freezes Up in Port Waters After Baltimore Bridge Collapse
2024-03-26 - U.S. port of Baltimore traffic was suspended until further notice following a bridge collapse. At least 13 vessels expected to load coal were anchored near the port at the time of the incident.
Segrist: The LNG Pause and a Big, Dumb Question
2024-04-25 - In trying to understand the White House’s decision to pause LNG export permits and wondering if it’s just a red herring, one big, dumb question must be asked.
Exclusive: Chevron Balancing Low Carbon Intensity, Global Oil, Gas Needs
2024-03-28 - Colin Parfitt, president of midstream at Chevron, discusses how the company continues to grow its traditional oil and gas business while focusing on growing its new energies production, in this Hart Energy Exclusive interview.
Imperial Expects TMX to Tighten Differentials, Raise Heavy Crude Prices
2024-02-06 - Imperial Oil expects the completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion to tighten WCS and WTI light and heavy oil differentials and boost its access to more lucrative markets in 2024.
Carlson: $17B Chesapeake, Southwestern Merger Leaves Midstream Hanging
2024-02-09 - East Daley Analytics expects the $17 billion Chesapeake and Southwestern merger to shift the risk and reward outlook for several midstream services providers.





