The global effort to slow climate change by reducing greenhouse-gas emissions got a $30 billion boost as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) announced the establishment of a fund called ALTÉRRA, with asset managers Blackrock, Brookfield and TPG signing on as partners.
The UAE, host of COP28, underway in Dubai, announced the commitment on Dec. 1 amid concerns about hitting emissions targets, continued reliance on fossil fuels and access to capital, including for the Global South. ALTÉRRA, dubbed a “catalytic climate vehicle,” was established by Lunate, an independent global investment manager based in Abu Dhabi, according to a news release.
COP28 President Sultan Al Jaber, who will chair ALTÉRRA’s board, said the fund “provides a transformational solution for attracting private capital. Its scale and structure will create a multiplier effect in climate focused investment, making it a vehicle like no other.”
Of the $30 billion commitment announced on Dec. 1, $25 billion will go toward scaling climate initiatives while $5 billion is intended to incentivize investment in the Global South where developing countries are heavily dependent on traditional forms of energy despite an abundance of opportunities for renewables.
Part of the initial capital investment has been set aside to develop more than 6 gigawatts (GW) of new clean energy capacity in India, including construction of 1.2 GW of wind and solar projects expected to begin production by 2025, the release stated. The fund and its partners are also considering an African development platform with more than 5 GW of onshore wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) energy projects as well as a rural electrification platform in Latin America capable of providing electricity to more than 1 million people.
ALTÉRRA aims to mobilize $250 billion globally by 2030, steering “private markets towards climate investments and focus on transforming emerging markets and developing economies, where traditional investment has been lacking due to the higher perceived risks across those geographies,” the release stated.
Here’s a look at other renewable energy project news this week:
COP28 Kicks Off with Climate Disaster Fund Victory
EQT CEO Toby Rice: Energy Transition Requires ‘Unleashing US LNG’
CNX Banking on Built-in Customer Base for Hydrogen [WATCH]
TotalEnergies Acquires Stake in Morocco-UK Renewables Project
Energy storage
American Lithium Looks to Fast-track Lithium Project in Peru
Canada-based American Lithium Corp. said Nov. 28 it submitted ahead of schedule the semi-detailed environmental impact assessment (EIA) for its Falchani Lithium project in southern Peru to the country’s energy and mines.
The company said it anticipates regulatory approval in the coming months. Approval would enable the fast-tracking of permits to build the mine, processing facilities and tailings disposal, American Lithium said in a news release.
The EIA process was launched during Peru’s prior administration, described by American Lithium’s CEO Simon Clarke as a “difficult time for permitting in Peru.” The arrest and removal of former Peruvian President Pedro Castillo in late 2022 led to violent protests in Peru. This year Dina Boluarte stepped into the presidential role. Peru is among the world’s largest producers of copper.
“With this approval, we will now be able to complete our PFS [pre-feasibility study] and move rapidly into the mine permitting process,” Clarke said in a news release, acknowledging support from new authorities in helping move the project forward.
If all regulatory approvals are gained, the company will be cleared to drill up to 420 drill platforms with no additional drill permits required. Following the filing of the PFS, next steps include filing the final EIA study, which the company said will enable construction and production.
India Launches First Part of $5.4B Critical Minerals Auction
India on Nov. 29 launched the first part of its critical minerals auction worth an estimated 450 billion rupees (US$5.40 billion), the country’s mines minister said.
Mines Minister Pralhad Joshi said the auctions would be held in eight states, including Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Jammu and Kashmir and would include minerals such as lithium, potash, vanadium, graphite, and rare earth elements.
“I also take this opportunity to invite prospective bidders from across the globe to participate,” Joshi said at the launch.
The first tranche, which will end on Feb. 20, will auction 20 blocks and is part of a planned auction of 100 blocks.
The government has also taken up 125 projects to explore critical minerals in the country, the country’s mining secretary V. L. Kantha Rao said at the launch event.
The Indian government in June listed 30 minerals, including nickel, titanium, vanadium and tungsten as critical to drive its clean energy push. The federal government had previously listed 12 strategic minerals, including lithium—a critical raw material for electric vehicle batteries.
Lithium reserves were discovered earlier this year in the federally administered region of Jammu and Kashmir. These reserves would be auctioned as part of the first tranche, Joshi said Nov. 29. India will also announce the acquisition of lithium blocks in Australia and Argentina in a month or two, he said at the event.
RELATED
Electra Battery, Rock Tech Sign MOU for Recycled Lithium Supply
Geothermal
Fervo Energy, Partner Google Crank Up Enhanced Geothermal Plant

Geothermal startup Fervo Energy begun delivering carbon-free electricity from its enhanced geothermal plant to Nevada’s power grid, supplying power to Google’s Cloud region in Las Vegas, the tech giant said on Nov. 28.
Fervo applied drilling techniques used in the oil and gas industry for the 3.5-megawatt (MW) Project Red, which reached vertical depths of about 8,000 ft and about 4,000 ft horizontally to harness heat.
The Houston-based company drilled a first-of-its-kind enhanced geothermal system horizontal double-well system with an injection and production well pair into a high-temperature, hard rock geothermal formation to capture heat. That heat is used to generate steam, which produces electricity. The process is also guided by real-time data on flow, temperature and performance gathered from fiber optic cables downhole.
“The result is a geothermal plant that can produce round-the-clock CFE [carbon-free energy] using less land than other clean energy sources and drawing on skills, knowledge, and supply chains that exist in other industries,” Google said. “From our early commitment to support the project’s development to its successful completion, we’ve worked closely with Fervo to overcome obstacles and prove that this technology can work.”
Google partnered with Fervo in 2021. The technology company aims to operate its data centers and office campuses on carbon-free energy by 2030. In September, the company also announced a partnership with Project Innerspace, an organization committed to advancing geothermal energy worldwide. Their efforts will include developing a global geothermal resource mapping and assessment tool.
Hydrogen
Cemvita, ChampionX Partner to Advance Gold Hydrogen Production
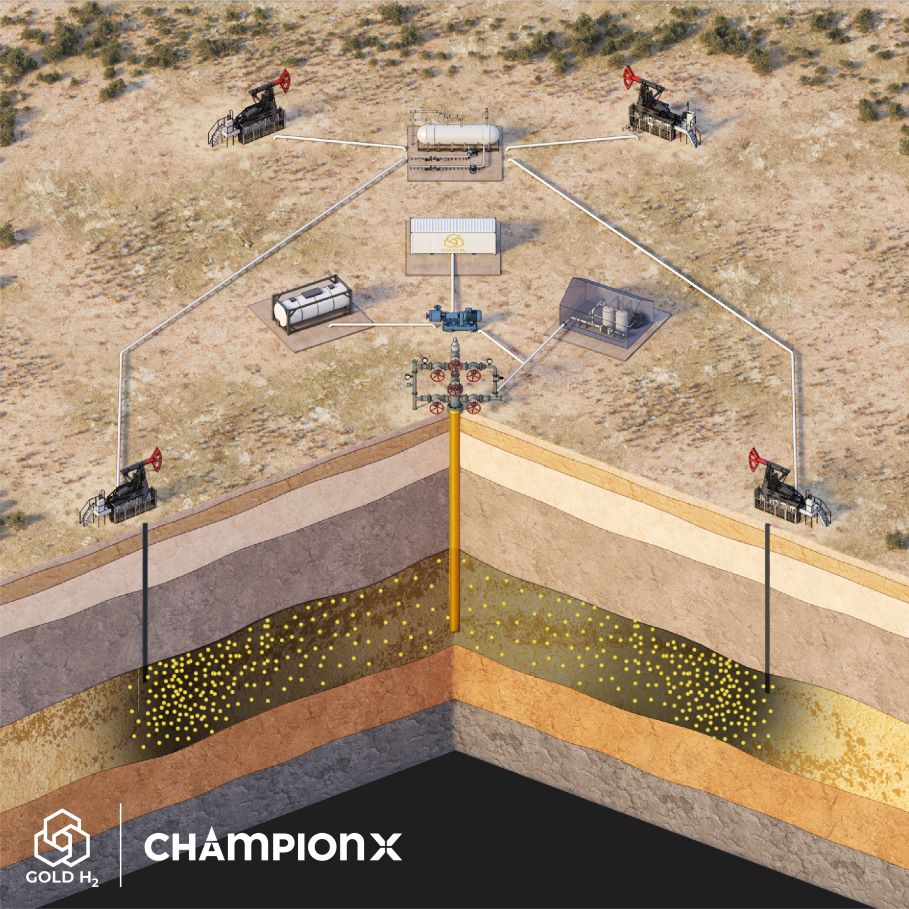
Oilfield technology provider ChampionX Corp. partnered with Cemvita Factory subsidiary Gold H2 Inc. (GH2) on field trials of GH2’s technology that uses microorganisms to produce “gold hydrogen” from depleted oil reservoirs, according to a Nov. 28 news release.
The companies aim to advance subsurface hydrogen production by bringing together GH2’s technology with ChampionX’s expertise in chemical technologies.
“The collaboration between GH2 and ChampionX has [the] potential to push the energy transition forward by driving innovation in applied microbiology and oil and gas operations,” the release stated. “GH2’s novel technology, complemented with ChampionX’s production expertise, provides a strong foundation for testing this technology.”
The partnership follows Cemvita’s successful Permian Basin field test in 2022 that demonstrated gold hydrogen production in situ.
RELATED
Drilling for ‘Gold’ Hydrogen in the Permian Basin
Technip Energies, John Cockerill Form Green Hydrogen, Power-to-X Company
France’s Technip Energies teamed up with Belgium-based John Cockerill, a designer and electrolyzer manufacturer, to form a company dedicated to integrated green hydrogen and Power-to-X projects, according to a Nov. 30 news release.
Called Rely, the company is an asset-light joint venture on a mission to decarbonize hard-to-abate industries.
Rely, using a standardized approach, will offer end-to-end large-scale solutions ranging from pre-final investment decision services—such as technical and financial advisory—to proprietary technologies, project execution and operation and maintenance, the release stated.
Rely was formed as the energy industry works to scale green hydrogen, green ammonia and other sustainable fuels.
“We’re determined to develop a portfolio of technologies that will drive down costs over the long haul. This is just the beginning of the story,” Technip Energies CEO Arnaud Pieton said in the release.
Rely is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. Technip Energies holds a 60% interest in Rely and John Cockerill 40%.
H2SITE, Gold Hydrogen Sign MOU for Natural Hydrogen Plant in Australia
Hydrogen tech company H2SITE and Gold Hydrogen signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a natural hydrogen pilot plant on the Yorke Peninsula, South Australia, according to a Nov. 26 press release.
The project represents a step forward in the natural hydrogen space, with one of the first wells showcasing unprecedented levels of H2 concentration, the release stated.
According to the release, white, natural or geologic hydrogen is naturally produced in the Earth’s crust as a source of energy, without a carbon footprint. Although it holds great decarbonization potential by reducing hydrogen costs, the technology requires development.
Utilizing H2SITE’s advanced membrane separation technology, the plant aims to recover over 95% of the available hydrogen while separating co-products such as helium.
“The collaboration with Gold Hydrogen underscores our shared commitment to the natural hydrogen market growth,” said Andres Galnares, CEO of H2SITE. “H2SITE is thrilled to contribute with its membrane separation technology, enabling sustainable and cost-efficient hydrogen production.”
H2SITE also announced on Nov. 24 the development of a new method for the company to produce hydrogen for power—an ammonia cracker to be used aboard ships. The ammonia cracking process involves purification to remove any traces of ammonia to deliver high-purity hydrogen to fuel cells.
The technology will first be used on the Bertha B, a supply ship sailing off the Gulf of Biscay.
Solar
Acciona Energia Taps India’s Waaree for More Solar PV Modules
Spain’s Acciona Energia has reached a three-year deal with India’s Waaree Energies to supply an additional 1.5 GW of solar PV modules for projects in the U.S., according to a news release.
As part of the agreement announced Nov. 27, Waaree will supply its N type TOPCON modules for projects being developed by Acciona in the U.S. from 2024 to 2026. The solar PV manufacturer has already delivered 850 MW of solar PV modules—monocrystalline passivated emitter and rear cell panels—for solar projects in Fort Bend and Wharton counties, Texas; High Point, Illinois; and Union, Ohio.
“At a time when the U.S. solar sector has faced supply chain challenges, Waaree has showcased its ability to deliver reliable module supplies while demonstrating a commitment toward maintaining product quality standards,” Sunil Rathi, interim CEO and board member, Waaree Solar Americas Inc., said in the news release.
The deal came as solar activity in the U.S. continues to grow. In the first half of 2023, solar power accounted for 5.9 GW of the 16.8 GW of utility-scale electric generating capacity additions in the U.S., according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. More than half of the 35.2 GW of new capacity expected in the second half of 2023 is solar.
So far this year, Waaree Energies has supplied more than 4 GW of solar modules to the U.S.
BP Buys Remaining Lightsource Stake for $320 Million
BP agreed to take full ownership of solar company Lightsource BP by acquiring the company’s 50.03% remaining interest, according to a Nov. 30 press release.
Under the agreement, BP will acquire the remaining stake in Lightsource from the company’s founders, management and staff. The parties agreed on a base equity value of £254 million (US$321 million) for the 50.03% interest, according to the release.
For full-year 2022, Lightsource BP reported underlying EBITDA of £287 million (US$ 362.9 million). On the transaction’s effective date of Dec. 31, 2022, the company had corporate level debt adjusted for cash of £1.5 billion (US$1.9 billion), excluding project finance. The transaction is anticipated to close mid-2024.
As part of the deal, BP will consolidate Lightsource BP’s net debt and an existing $900 million loan guarantee issued by BP related to Lightsource BP will be removed from BP’s reported adjusted debt.
BP said full ownership will enable the company to further scale up Lightsource BP and create additional value by applying complementary capabilities and strengths—including in finance and trading—to the business. BP will continue to target double-digit equity returns from the business.
Following the deal’s completion, BP intends to maintain Lightsource’s independent brand and organization. In early 2024, Joaquin Oliveira, who now serves as BP’s senior vice president of finance for gas and low carbon energy, will take on the role of co-CEO of Lightsource. Oliveira has been a non-executive director of Lightsource BP for more than two years.
“This is a natural evolution of the partnership we have built over the past six years—now we will be able to take Lightsource BP to the next level of profitable growth and performance,” Dotzenrath said.
Wind
South Korea Grants Ørsted License for Offshore Wind Project
South Korean authorities granted Ørsted a 1.6-GW electricity business license, enabling the company to develop the Incheon offshore wind project, according to a Nov. 30 news release.
Located about 70 km off the coast of Incheon City, the project could provide enough renewable energy for more than 1 million Korean households and lower emissions by about 4 million tonnes annually, Ørsted said.
The electricity business license, approved by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy of Korea, marks the first for Ørsted in the country.
“Ørsted has unparalleled capabilities for delivering large-scale offshore wind power projects, and we have a strong track record working with Korean suppliers in our global portfolio over the past decade,” Per Mejnert Kristensen, senior vice president and president of the Asia-Pacific for Ørsted, said in the release. “This collaboration will ensure the Incheon project leads the way for a thriving offshore wind industry, capable of generating clean energy reliably, attracting long-term investments, and creating jobs in Korea.”
Next steps for the project include environmental impact assessments, site investigations and preparations for participating in Korea’s annual fixed-price wind auction, Ørsted said.
The project is expected to complete in the early 2030s, subject to a final investment decision.
RWE, Masdar to Co-develop Giant British Offshore Wind Project
Germany’s RWE signed an agreement with the UAE’s clean energy developer, known as Masdar, to develop a 3-GW wind project off the coast of Britain, capable of powering around 3 million homes, the companies said Dec. 1
The announcement came after British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak said at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai that the two companies had committed to invest up to 11 billion pounds (US$13.9 billion) in the project.
Britain, which is already the world’s second-largest offshore wind market after China, is seeking to ramp up its capacity to 50 GW by 2030 from around 14 GW now, to help meet its climate targets and boost energy security.
Construction of the Dogger Bank South offshore wind project in the North Sea could start in 2025, with first power of around 800 MW by 2029 and full capacity by late 2031, RWE said.
The project, in which RWE will have a 51% share and Masdar a 49% share, is made up of two 1.5 GW windfarms.
RWE did not disclose any details on the likely cost of the project.
Masdar said its decision to acquire the 49% stake in the project from RWE was part of an 11-billion-pound investment in Britain’s renewable sector.
Hart Energy Staff and Reuters contributed to this report.
Recommended Reading
NOV Announces $1B Repurchase Program, Ups Dividend
2024-04-26 - NOV expects to increase its quarterly cash dividend on its common stock by 50% to $0.075 per share from $0.05 per share.
Repsol to Drop Marcellus Rig in June
2024-04-26 - Spain’s Repsol plans to drop its Marcellus Shale rig in June and reduce capex in the play due to the current U.S. gas price environment, CEO Josu Jon Imaz told analysts during a quarterly webcast.
US Drillers Cut Most Oil Rigs in a Week Since November
2024-04-26 - The number of oil rigs fell by five to 506 this week, while gas rigs fell by one to 105, their lowest since December 2021.
CNX, Appalachia Peers Defer Completions as NatGas Prices Languish
2024-04-25 - Henry Hub blues: CNX Resources and other Appalachia producers are slashing production and deferring well completions as natural gas spot prices hover near record lows.
Chevron’s Tengiz Oil Field Operations Start Up in Kazakhstan
2024-04-25 - The final phase of Chevron’s project will produce about 260,000 bbl/d.





