
The offshore deepwater Perdido platform located in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico. (Source: Royal Dutch Shell Plc)
Royal Dutch Shell said May 11 it has struck oil pay at the Leopard prospect in the deepwater U.S. Gulf of Mexico (GoM), proving the mature province still has plenty to give explorers.
Drilled by the Transocean Deepwater Thalassa in Alaminos Canyon Block 691, the Leopard well hit more than 600 ft of net oil pay at multiple levels, Shell said in a news release. The discovery was made in a lush oil-producing area known as the Perdido Corridor, located in the northwestern part of the GoM.
“Evaluation is ongoing to further assess commerciality and define development options,” Shell spokesperson Cindy Babski told Hart Energy.
Serving as operator, Shell owns a 50% stake in Leopard and partner Chevron USA Inc. holds the remaining interest. The company generally does not share details on estimated discovered resource volumes for discoveries.
The Leopard discovery was made in about 6,800 ft of water. It joins the nearby Perdido host, the production hub about 33 miles away for the Great White, Tobago and Silvertip fields. It’s also located near the 2019 Blacktip discovery in the Wilcox formation and 2018 Whale Paleogene discovery, for which Shell said it is moving toward a final investment decision this year.
RELATED
Shell Oil Plans More Drilling at Blacktip Prospect
How Shell Hid A Whale Before Placing Mexican Oil Bet
Leopard, described as a “significant” discovery, was called an exciting addition to the company’s portfolio by Paul Goodfellow, deepwater executive vice president for Shell.
“With our U.S. Gulf of Mexico production among the lowest GHG (greenhouse-gas) intensity in the world, Shell remains confident about the GoM and this latest discovery will help us deliver on our strategy to focus on valuable, high margin barrels as we sustain material upstream cash flows into the 2030s,” Goodfellow said in a company statement.
Shell is among the largest deepwater leaseholders in the GoM, where the company produces about 150 million boe per year and operates nine deepwater production hubs, including the Perdido hub.
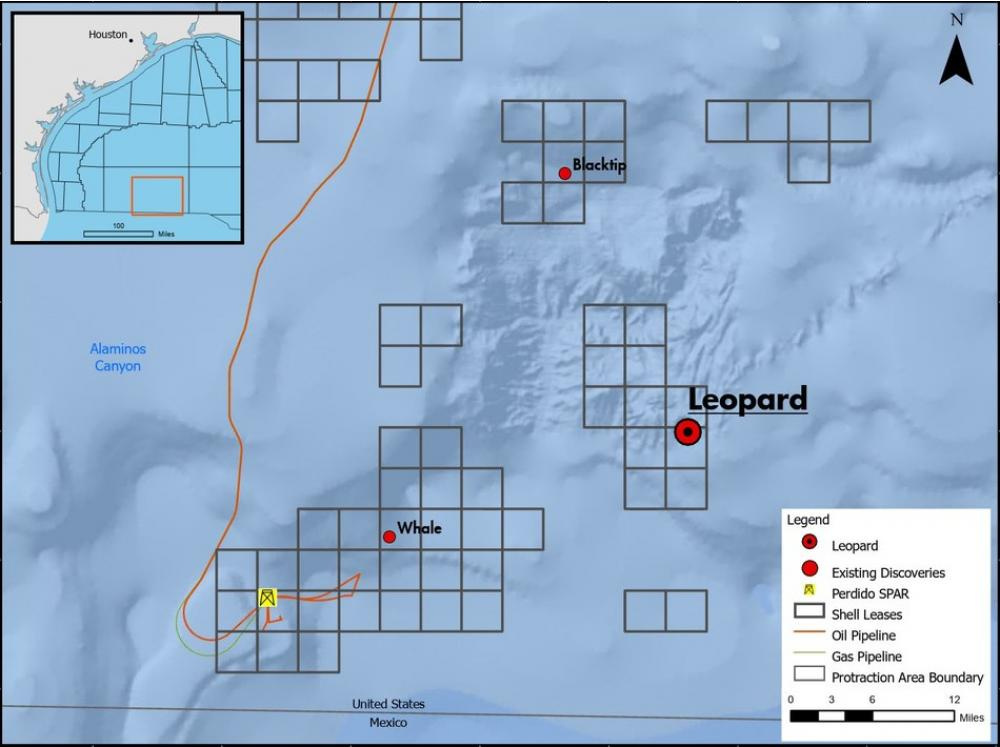
Perdido opened a new deepwater oil frontier in the Lower Tertiary/Paleogene when it reached first oil in 2010. Since then, the Perdido Fold Belt area has been a magnet for companies looking for hydrocarbon resources, including in Mexican waters where state-owned Pemex proved commercial oil volumes with its Trion discovery in 2012—now operated by BHP Billiton—followed by several others.
Recommended Reading
Venture Global Gets FERC Nod to Process Gas for LNG
2024-04-23 - Venture Global’s massive export terminal will change natural gas flows across the Gulf of Mexico but its Plaquemines LNG export terminal may still be years away from delivering LNG to long-term customers.
US EPA Expected to Drop Hydrogen from Power Plant Rule, Sources Say
2024-04-22 - The move reflects skepticism within the U.S. government that the technology will develop quickly enough to become a significant tool to decarbonize the electricity industry.
Exclusive: ‘Regulatory Tsunami’ a Top Priority for American Producers, Says AXPC’s Bradbury
2024-04-22 - Regulatory considerations have significant implications for how oil and gas companies evaluate risk, and it’s a top priority for American energy producers right now, said American Exploration & Production Council CEO Anne Bradbury at CERAWeek by S&P Global.
Biden Administration Criticized for Limits to Arctic Oil, Gas Drilling
2024-04-19 - The Bureau of Land Management is limiting new oil and gas leasing in the Arctic and also shut down a road proposal for industrial mining purposes.
Exclusive: The Politics, Realities and Benefits of Natural Gas
2024-04-19 - Replacing just 5% of coal-fired power plants with U.S. LNG — even at average methane and greenhouse-gas emissions intensity — could reduce energy sector emissions by 30% globally, says Chris Treanor, PAGE Coalition executive director.





