Another week means more action on energy transition.
This week, the push to strengthen the hydrogen market got a $5 billion boost in Europe and a company focused on hydrogen fuel cells shed light on the technology’s efficiency compared to diesel.
Prairie Lithium is finding synergies in the oil field as it saves money on building new wells by seeking out abandoned ones in its quest to find more lithium, a key component in rechargeable batteries.
Other companies are making moves in solar: EDP Renewables North America started construction on a solar park in Texas, while Amazon said it will build its first solar farms in Brazil, India, Poland and Louisiana.
Here’s a look at some of this week’s renewable energy news.
Batteries
Prairie Acquires Soon-to-be Abandoned Oil Wells for Lithium Research
Prairie Lithium Corp. said Sept. 21 it has acquired three more oil wells that were set to be abandoned by an oil producer in Saskatchewan, Canada, as it seeks lithium.
The Williston Basin lithium resource and technology developer said it purchased the wells for $1 each. The acquisition comes after Prairie assessed whether the wells could be deepened to the base of the Duperow Formation to hit the company’s primary lithium production target and whether the well could be perforated to test a potential water disposal zone.
“These agreements highlight the synergies occurring between the emerging lithium and geothermal sectors, and the robust oil industry in Saskatchewan,” Prairie Lithium said in the release.
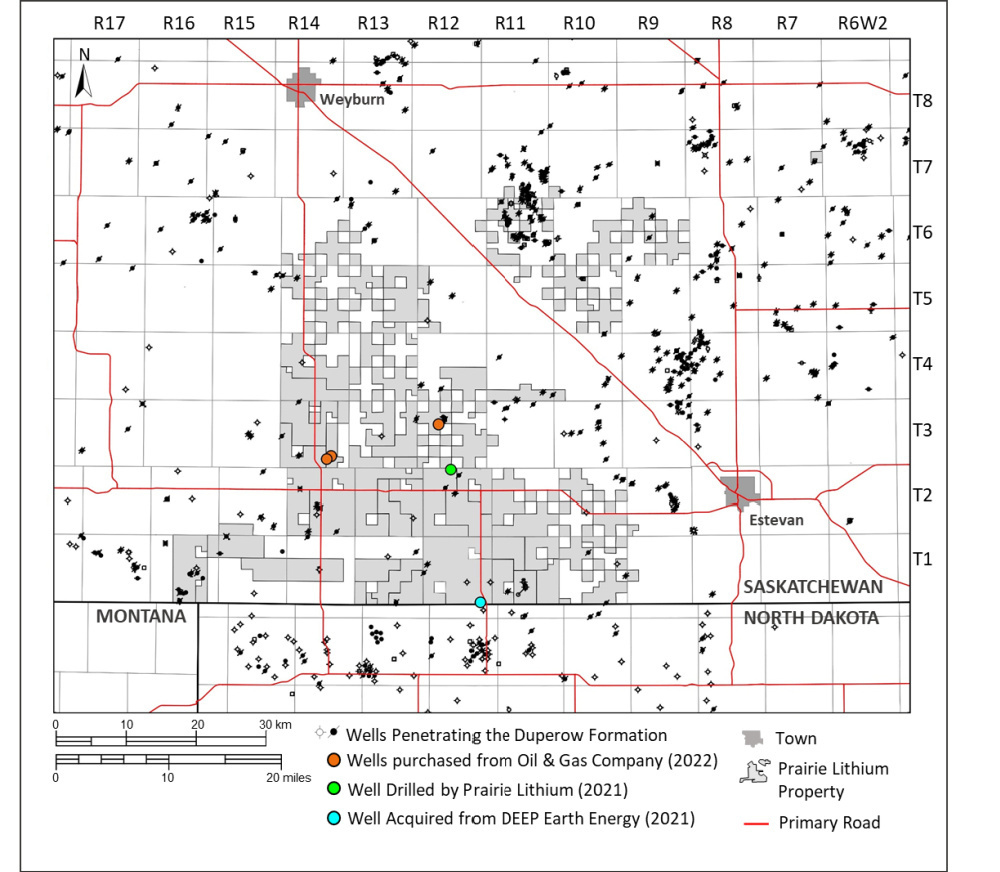
The company’s field will include production, injection and pressure monitoring wells, it said in the release. If regulators approve, the company said it plans to deepen and test one of the wells acquired through this deal by an additional 180 m.
“After the drilling is completed, the well will be cased then perforated within the zones of interest,” it said. “A three-day pump test, followed by a four to six-day build-up period will be completed to understand the productivity of the well across the zones of interest.
The company said it also hopes to produce lithium-rich brine for ongoing direct lithium extraction testing and research.
Oil Giants Join Forces with SAIC, CATL in Swappable Battery JV
China’s top oil and gas producer PetroChina has joined leading auto group SAIC Motor Corp. and battery firm CATL in setting up a joint venture to supply swappable batteries for electric vehicles, parent company CNPC said Sept. 22.
CNPC did not provide the details of stakeholding but official business registration portal shows that the new venture, Shanghai Jieneng Smart Power New Energy Technology Co. Ltd., is 37.5% owned by SAIC Motor while PetroChina and CATL each hold 12.5% in the venture. Second-largest oil and gas major Sinopec owns 25%.
With its business focusing on leasing power batteries, the Shanghai-based firm will also research swappable battery technology as well as provide big data services, CNPC said.
China’s state energy giants are expanding their investment in low-carbon businesses including renewables, hydrogen and electric mobility as part of the country’s goal to be carbon neutral by 2060.
CNPC aims to build over 1,000 charging stations by 2025 in China, having built 203 so far, the company said.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information (MIIT), a major supporter of battery swapping, aims to have more than 100,000 battery-swappable vehicles and more than 1,000 swap stations by 2023.
Geothermal
Eavor, KCA Deutag Team Up for German Geothermal Power Project
Eavor Erdwärme Geretsried GmbH has tapped drilling and engineering company KCA Deutag for two rigs to build Eavor’s first commercial Eavor-Loop system in Germany, according to a news release.
Construction of the closed-loop geothermal system, which uses conduction to harness heat from the earth’s subsurface, is expected to begin in 2023 utilizing two of KCA Deutag’s largest rigs in Europe.
“We use it to scale up geothermal energy through the successful development of closed-loop systems and thereby making it a key technology for energy transition and energy security plans in the future,” Eavor Country Manager Daniel Moelk said in the release.
Plans are to drill separate wellbores that will intersect about 5,000 m underground to enable continuous water circulation, drawing heat from the subsurface rock and returning energy to the surface, the news release stated. After the first system is installed, three more are planned to extend the subsurface length.
“It is a revolutionary design, with an estimated continuous output of up to 9 MWe and up to 65 MW thermal capacity in the first development phase with the possibility to heat or power ~30,000 homes or businesses,” KCA said in the release.
Hydrogen
Air Products Plans for Second Liquid Hydrogen Plant in Rotterdam
Pennsylvania-headquartered Air Products plans to build a second hydrogen liquefaction plant in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, doubling its capacity in Europe, the company said Sept. 21.
Air Products said liquid hydrogen produced at the plant will supply high tech industries and the mobility market as well as contribute to the decarbonization of heavy-duty vehicles in Europe.
The plant is scheduled to begin operations in 2025.
EU OKs $5.2 Billion In State Aid for Hydrogen Development
The European Commission has approved about $5.15 billion in public funds by 12 member states for hydrogen R&D and construction of infrastructure as part of its Important Project of Common European Interest (IPCEI) Hy2Use program.
The funding could unlock an additional €7 billion in private investments, the EU said in a news release.
“As part of this IPCEI, 29 companies with activities in one or more Member States, including small and medium-sized enterprises (‘SMEs') and start-ups, will participate in 35 projects,” it said.
The projects include several with large-scale electrolyzers that could become operation between 2024 and 2026 with other technologies deployed between 2026 and 2027.
The IPCEI, slated for completion in 2036, “IPCEI is expected to boost the supply of renewable and low-carbon hydrogen, thereby reducing dependency on the supply of natural gas,” the release said.
Loop Calls New Hydrogen Fuel Cell More Efficient Than Diesel Engine
Hydrogen fuel cell maker Loop Energy said on Sept. 18 that its latest cell system can deliver better fuel economy than a diesel engine at current price levels.
The Burnaby, British Columbia-based company said that—based on a pan-European diesel cost of $1.91 per liter on Sept. 5 and $10 per kg of hydrogen—a truck could travel just over 111 miles (179 km) on $100 worth of fuel using its new S1,200 hydrogen fuel cell system versus a little over 109 miles for an equivalent diesel truck.
As the auto industry makes the shift to zero-emission electric vehicles (EVs), big freight truck makers like Daimler Truck and Volvo are investing heavily in hydrogen fuel cells to haul freight long distances because batteries weigh too much to make electric trucks viable.
Hydrogen fuel cells run hydrogen through a catalyst that produces energy and heat to power a small battery that drives the truck—the only emission from these cells is water.
Hydrogen fuel cells have faced two challenges for broad adoption: they have so far been less efficient than diesel and fueling infrastructure in Europe is virtually non-existent.
Loop Energy CEO Ben Nyland said the new cell system essentially addresses the first of those challenges.
“This brings the future forward,” Nyland told Reuters. “This product delivers the economics that are needed for adoption today.”
Nyland said that Loop Energy aims to provide the fuel cell system to startup truck makers and as part of hydrogen powertrains provided to big truck makers by major suppliers.
South Korean Firms to Set Up Green Energy Hub in Australia
Three major South Korean groups said Sept. 21 they hope to build a green energy export hub in Australia’s Queensland state, aiming to produce a million tonnes of green ammonia annually for export by 2032.
The Han-Ho Hydrogen Consortium, launched on Sept. 21 by Korea Zinc, petrochemicals group Hanwha Impact Corp. and SK Gas, plans to build up to 3 GW of renewable energy capacity in Collinsville in Queensland.
That electricity would be used to power electrolyzers that split water and produce green hydrogen, which would then be used to produce ammonia for export to South Korea, the Queensland government and the companies said.
The statement did not mention an estimated cost for the huge project.
Solar
Amazon Strengthens Renewable Energy Portfolio with 71 Projects
Tech powerhouse Amazon is entering the solar energy scene in Brazil, India and Poland as part of a global expansion of the company’s renewable energy portfolio.
Amazon said Sept. 21 it is adding 2.7 GW of clean energy capacity across 71 projects, including wind and solar, to power its offices, data and fulfillment centers, and stores. The expansion is expected to contribute to a renewable energy portfolio capable of generating 50,000 GW hours of clean energy—enough to power annually 4.6 million U.S. home, Amazon said in a news release.
“Around the world, countries are looking to accelerate the transition to a clean energy economy,” Amazon Web Services CEO Adam Selipsky said in the release, “and continued investments like ours can help accelerate their journey as we all work together to mitigate the impacts of climate change.”
The projects include three large-scale solar farms in India, a 122-MW solar farm in Brazil and a utility-scale solar project in Poland. The company is also pursuing its first two renewable energy projects in Louisiana, part of a 1-GW clean energy capacity addition in the Southeastern U.S.
Amazon said it had reached 85% renewable energy across its business by year-end 2021. The company, among the world’s largest corporate buyers of renewable energy, has nearly 380 renewable energy projects worldwide.
EDP Begins Building 240-MW Solar Park In Texas
EDP Renewables North America has begun construction of the 240-MW Cattlemen Solar Park in Milam County, Texas, its first in the state.
The solar park will also be the largest in the company’s North American portfolio, it said.
The facility, scheduled to go online in 2023, will generate the equivalent of the energy consumption of more than 37,000 average homes, the company said in a news release Sept. 20.
The developer has already sealed two long-term commercial agreements for the project: one with Meta for 156 MW and one with Bristol Myers Squibb for 60 MW.
Wind
Portugal Ups Debut Offshore Wind Auction Target to 10 GW
Portugal has raised the target for its debut offshore wind power auction to 10 GW, Environment Minister Duarte Cordeiro said Sept. 21, aiming to “move faster” on the country’s energy transition.
In June, Cordeiro put the capacity on offer at the auction due next year at 6-8 GW, which was already double the government’s target at the start of 2022.
The energy crisis caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is forcing countries to bet more on new technologies to boost renewable energy generation, such as wind and solar, which was already happening as part of a global shift from fossil fuels.
Cordeiro said technical details and the list of coastal locations were being prepared.
“We have urgency and we’re going to accelerate everything that is renewable. We want to launch a large offshore wind auction and our ambition now is to reach 10 GW of capacity,” he told a parliamentary committee.
Floating wind technology, seen as the final frontier in the offshore wind industry, has gained traction in countries such as Britain, France and parts of south-east Asia. Portugal has a small, 25-MW floating wind project off its Atlantic coast.
Portugal has 7.3 GW of hydroelectric capacity and 5.6 GW of onshore wind, which together represent 83% of its total installed capacity.
Mercedes-Benz to Build Wind Farm in Northwestern Germany
Mercedes-Benz is planning to build a wind farm in the northwestern German state of Lower Saxony, by 2025 that is able to produce 100 MW of electricity, equivalent to over 15% of the carmaker’s annual demand in Germany, it said Sept. 19.
Mercedes will invest a three-digit million figure in a power purchase agreement with an as-yet-unnamed partner to buy the electricity generated by the turbines, the carmaker said.
It is also examining together with local authorities whether it could put solar panels onto the remaining space in the 800-hectare piece of land in Papenburg, a test track owned by the carmaker.
Reuters contributed to this article.
Recommended Reading
Less Heisenberg Uncertainty with Appraisal Wells
2024-03-21 - Equinor proves Heisenberg in the North Sea holds 25 MMboe to 56 MMboe, and studies are underway for a potential fast-track tieback development.
OKEA Fast-tracking North Sea’s Brasse Tieback to Brage
2024-04-08 - OKEA expects first production in 2027 and has signed contracts with Aker Solutions, Subsea7 and OneSubsea.
Sinopec Brings West Sichuan Gas Field Onstream
2024-03-14 - The 100 Bcm sour gas onshore field, West Sichuan Gas Field, is expected to produce 2 Bcm per year.
Orange Basin Serves Up More Light Oil
2024-03-15 - Galp’s Mopane-2X exploration well offshore Namibia found a significant column of hydrocarbons, and the operator is assessing commerciality of the discovery.
E&P Highlights: March 11, 2024
2024-03-11 - Here’s a roundup of the latest E&P headlines, including a new bid round offshore Bangladesh and new contract awards.





