A consortium led by Cerulean Winds and Frontier Power plans to build a gigantic $25 billion floating wind-powered offshore electrical grid that oil and gas producers could use to power their operations in the North Sea.
Called the North Sea Renewables Grid, the offshore integrated green power and transmission system will include three 333 km sites with hundreds of floating turbines, Cerulean Winds said May 4. News of the planned subsea grid came after Cerulean secured three seabed leases offered during the recent Crown Estate Scotland INTOG round in March.
The consortium—which also includes NOV, Siemens Gamesa, Siemens Energy, DEME and Worley—is initially focusing on providing power to oil and gas operators that are aiming to hit emissions reductions targets.
“We recognize that to achieve meaningful reductions at the pace required, a reliable basin-wide approach is needed that they can plug into when they are ready for affordable power,” Dan Jackson, founding director of Cerulean Winds, said in a statement. “Early oil and gas electrification supports the country’s energy security, net zero action and delivers huge benefits to the supply chain and economy, creating 10,000 jobs.”
Developers see the infrastructure powering what Jackson called the “next phase of the North Sea’s life.”
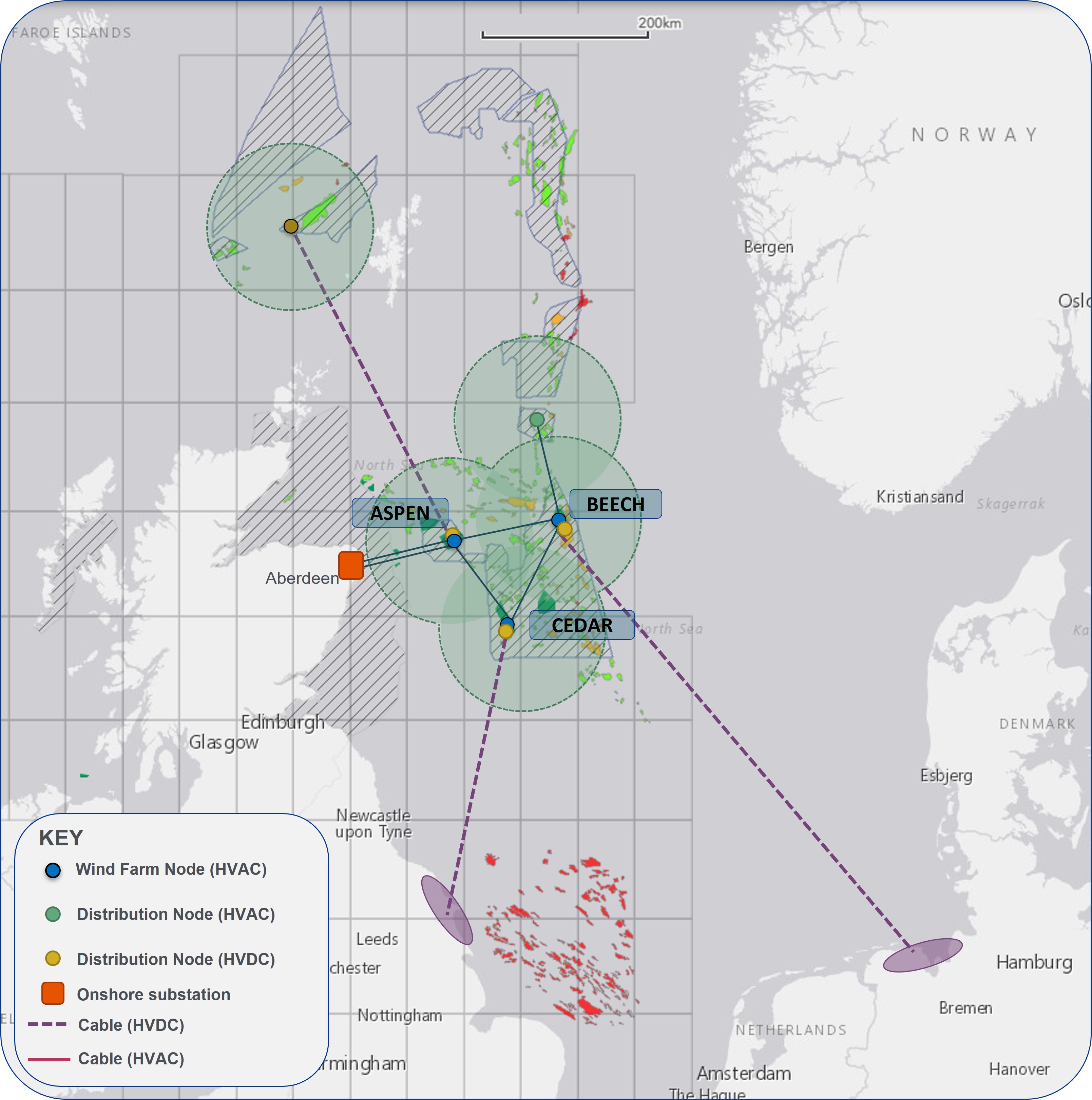
Located within 100 km of each other, the wind farms will each be connected to form an offshore ring around the Central North Sea, said Humza Malik, founding partner of Frontier Power.
“The scale allows for offtake to other parts of the North Sea through a new High Voltage Direct Current (HDVC) network,” Malik said. “For the oil and gas companies, this diversity of offtake provides robustness to the scheme and added flexibility.”
Future plans will focus on exporting green power to grids in southern U.K. and Europe, according to a news release.
Here’s a look at some of this week’s other renewable energy news.
RELATED
OTC: Panelists Talk Floating Wind Challenges, Solutions
U.S. Cities Turn Old Garbage Dumps Into Solar Parks
OTC: OGCI Raising Second Investment Fund for Decarbonization
Geothermal
DOE Awards Grant to Advance Geothermal
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Geothermal Technologies Office (GTO) has awarded funds to a consortium formed by Project Innerspace, the Society of Petroleum Engineers and Geothermal Rising to advance geothermal energy based on lessons from the oil and gas industry.
The consortium landed a $165 million Geothermal Energy from Oil and Gas Demonstrated Engineering (GEODE) initiative grant. Project Innerspace said $10 million provided for the first year will go toward funding consortium members and more than 100 partners to “develop a roadmap to accelerate the growth and development of geothermal, leveraging expertise, technologies, and methods from the oil and gas industry.”
Up to $155 million more will go toward putting the plan into action.
“The oil and gas and geothermal industries have numerous similarities that provide exciting opportunities for geothermal expansion—from advances in drilling and well construction to co-production possibilities in existing oil and gas basins,” GTO said in a May 4 release. “GTO and the GEODE consortium will identify ways to access and apply the expertise, technologies, assets and workforce skills of the larger domestic oil and gas industry to overcome barriers for geothermal energy and encourage private investment.”
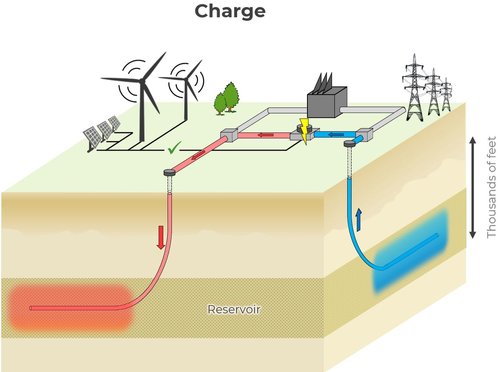
EarthBridge Acquires Texas Acreage For ‘GeoBattery’ Energy Storage
Texas-based geothermal company EarthBridge Energy said May 2 it has acquired acreage in West Texas to deploy geothermal energy storage technology.
The company’s GeoBattery technology stores excess energy from wind, solar or the grid in a subsurface reservoir, returning it to the grid when there is demand. The company is gearing up for its first application of the long-duration storage technology, which it says can store excess electricity for up to 1,000 hours or more.
“This marks an important step in EarthBridge’s strategy to deploy geothermal energy storage assets across the U.S. and adds a key project to our portfolio,” EarthBridge Energy CEO Derek Adams said in a statement.
Hydrogen
Electrolyzer Maker Nel Selects Michigan for New Gigafactory
Norway-headquartered Nel, a pure-play hydrogen technology company, plans to build an automated gigawatt-scale electrolyzer facility in Michigan.
The $400 million investment, announced May 3, comes amid heightened interest in using hydrogen to help reduce reliance on fossil fuels in order to lower emissions.
“The choice of Michigan is based on an overall assessment of what the state can offer in terms of financial incentives, access to a highly skilled workforce, and cooperation with universities, research institutions and strategic partners,” Nel CEO Håkon Volldal said in a news release. “I will also highlight the personal engagement from [Michigan] Gov. [Gretchen] Whitmer and her competent and service-minded team.”
The facility, which will follow the fully automated alkaline manufacturing concept invented at Herøya in Norway, will be capable of producing up to 4 gigawatts (GW) of alkaline and PEM electrolyzers, the company said. It added the company’s expansion of its Wallingford facility will play an important role in establishing a blueprint to scale up the production of PEM electrolyzers.
Nel has been working with General Motors, headquartered in Michigan, to lower costs of green hydrogen. The auto company is developing and commercializing hydrogen fuel cells and battery technologies. GM’s aim is to open new revenue streams geared toward the freight trucking, aerospace, power generation and locomotive sectors.
Massachusetts Selected as Site for EH2’s Gigafactory
Massachusetts-based Electric Hydogen Co. (EH2) has decided to open its first gigafactory in Devens, Massachusetts, the company said on May 4. The company has leased a 187,000-sq-foot facility.
“There are a lot of factory announcements in our industry, but not a lot of real capacity being built,” said EH2 CEO Raffi Garabedian. “We have a backlog of customer orders to fulfill and are moving quickly to build and ship the world’s most powerful electrolyzers.”
Eyeing an annual manufacturing capacity of 1.2 GW, the company said it plans to start producing 100-megawatt (MW) green hydrogen electrolyzers in first-quarter 2024.
Using hydrogen created with renewable electricity, the company is on a mission to help eliminate more than 30% of global greenhouse-gas emissions from hard-to-electrify industries. It also aims to lower costs using economies of scale
“Industrial sectors such as fertilizer and steel need new ways to reliably replace fossil resources at costs that work,” said David Eaglesham, EH2’s CTO and co-founder. “The machines we will produce at our new factory in Devens will have a transformational impact by enabling ultra-low-cost green hydrogen at an industrial scale.”
The new production tax credit in the Inflation Reduction Act combined with other incentives, including in the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, is improving the economics of hydrogen and boosting demand.
Solar
Senate Repeals Solar Panel Tariff Suspension, Biden Expected to Veto
The U.S. Senate on May 3 voted to repeal President Joe Biden’s suspension of tariffs on solar panels from four Southeast Asian nations, a measure aimed at supporting the small domestic manufacturing industry.
The final Senate vote was 56-41, with nine Democrats voting in favor.
Biden has vowed to veto the legislation, which passed the House of Representatives last week. It is not expected to have enough support to override a presidential veto.
The U.S. has been trying to strike a tricky balance between supporting the creation of a domestic solar supply chain while keeping cheap imports flowing to projects needed to move the U.S. away from its reliance on fossil fuels.
Biden, a Democrat, waived tariffs on solar imports from Malaysia, Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam for two years last June after solar project developers said they would increase their costs and freeze development.
Panels from the four nations, which host manufacturing facilities owned by Chinese companies, account for about 80% of U.S. supplies. Domestic producers say they cannot compete with the cheap products made overseas.
The House resolution that passed the Senate was introduced under the Congressional Review Act (CRA), a law that allows Congress to reverse federal agency rules. A CRA bill expires if it is not passed within 60 days of its introduction.
Proponents of the measure say the two-year suspension allows Chinese producers to avoid U.S. trade laws and prolongs an unfavorable market for domestic businesses.
“Developing our solar manufacturing industry is crucial to combating climate change, but we can’t do it if we don’t enforce the trade laws on the books,” Democratic Senator Tammy Baldwin said on Wednesday.
Top clean energy trade groups had called on members of Congress to oppose the measure. The Solar Energy Industries Association projected that its passage would result in cancellation of 14% of the industry’s planned new capacity this year and the loss of $4.2 billion in investment.
Repealing the suspension would “deal a devastating blow to the American solar industry, which will kill jobs, raise energy costs, and decrease our ability to achieve clean energy independence,” a group of senators led by Democratic Senator Jacky Rosen wrote in an open letter published on May 2.
Wind

BP Sticks with ONYX for Wind Farm Predictive Maintenance Technology
Predictive analytics provider ONYX Insight will deploy its predictive maintenance technology across BP Wind Energy’s U.S. onshore wind portfolio, according to a May 4 news release.
The five-year agreement continues a partnership between the two companies that started seven years ago.
“By leveraging ONYX’s technology, we can better understand the life span of turbine components at our wind farms, improve maintenance schedules, reduce costs and avoid breakdowns,” said Alistair Warwick, CEO BP Wind Energy. “This agreement helps BP Wind Energy remain a technology leader. It also supports our commitment to produce secure, affordable, lower-carbon energy while accelerating our net zero ambition.”
BP has nine onshore wind farms in Colorado, Idaho, Indiana, Kansas, Pennsylvania and South Dakota with a gross onshore wind generating capacity of 1.7 GW. Its largest onshore wind footprint is in Indiana, home to the Fowler Ridge 1, 2 and 3 wind farms that span more than 42,000 acres.
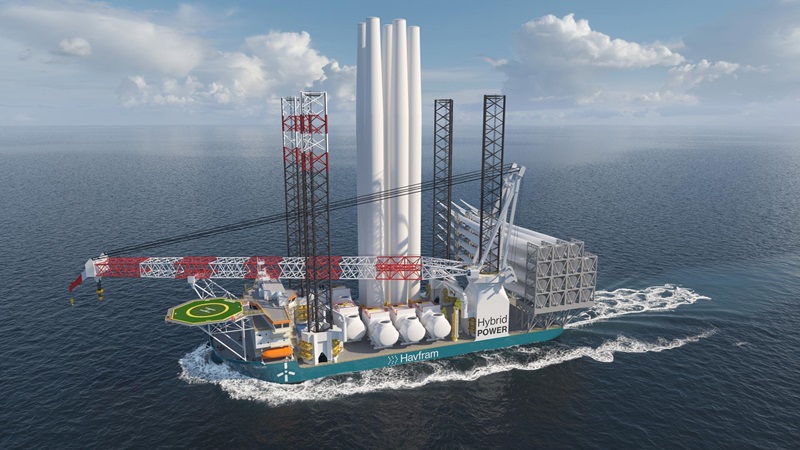

Havfram Selects NOV for Second Installation Vessel
Offshore wind developer Havfram has tapped NOV for its second wind installation jackup vessel, having signed a contract with CIMC Raffles for another GustoMSC NG-20000X.
The company’s first vessel is under construction, NOV said on May 5.
The GustoMSC installation vessel is considered one of the industry’s largest and sports a heavy lift crane that can install foundations weighing up to 3,000 tons.
NOV said the vessel is capable of installing wind turbines with tip heights greater than 300 m in water depths up to 70 m.
“Like the vessel currently under construction under the first contract, Havfram’s second self-propelled jack-up vessel will be equipped with the proven NOV variable-speed drive rack and pinion jacking systems, including the latest regenerative power system technology that feeds the generated power back into the vessel’s system,” the company said.
Reuters contributed to this article.
Recommended Reading
Excelerate Energy, Qatar Sign 15-year LNG Agreement
2024-01-29 - Excelerate agreed to purchase up to 1 million tonnes per anumm of LNG in Bangladesh from QatarEnergy.
UK’s Union Jack Oil to Expand into the Permian
2024-01-29 - In addition to its three mineral royalty acquisitions in the Permian, Union Jack Oil is also looking to expand into Oklahoma via joint ventures with Reach Oil & Gas Inc.
Permian Resources Continues Buying Spree in New Mexico
2024-01-30 - Permian Resources acquired two properties in New Mexico for approximately $175 million.
Eni, Vår Energi Wrap Up Acquisition of Neptune Energy Assets
2024-01-31 - Neptune retains its German operations, Vår takes over the Norwegian portfolio and Eni scoops up the rest of the assets under the $4.9 billion deal.
NOG Closes Utica Shale, Delaware Basin Acquisitions
2024-02-05 - Northern Oil and Gas’ Utica deal marks the entry of the non-op E&P in the shale play while it’s Delaware Basin acquisition extends its footprint in the Permian.






